Impact of the Strong Customer Authentication on E-commerce
What is 3D Secure?
3D Secure (3-domain secure) or also known as payer authentication is is an XML-based protocol designed to be an additional security step for online credit and debit card transactions and prevent fraud. It was first deployed by Visa and MasterCard and branded as “Verified by Visa” and “MasterCard SecureCode” respectively. Notably, other card networks also have developed this authentication tool- American Express has branded it “SafeKey”, Discover as “Discover ProtectBuy”, and JCB International as “J/Secure”.
It is a three-part process, in which three parties are engaged: the issuer, the acquirer, and the card network. This process is controlled by a piece of software that is installed on the website of merchant known as Merchant Plug In (MPI), which communicates directly with the card networks. The entire process with 3D Secure enabled looks as follows:
· The customer confirms the order and enters the payment card details at the checkout.
· The merchant website requests the directory server of card network via its MPI.
o When there is a new payment request at the payment gateway, the MPI is activated. The Merchant Plug In then contacts card network to verify if the card supports and is enlisted for 3D Secure. If the card is not enlisted, this means that either the financial institution that issued the card is not supporting 3D Secure or it means that the cardholder has not registered for the service. If 3D Secure is enabled, the MPI will redirect to authentication pop-up window, where cardholder will then identify himself/herself.
· The buyer is redirected to the website of the issuer and identifies him/herself.
· After the authentication, the buyer is redirected to the merchant website.
· The MPI of the payment gateway verifies the information:
o If the buyer has not authenticated him/herself, the payment is refused.
o If the buyer has authenticated him/herself, the payment gateway proceeds to the authorization request.
· The payment gateway returns the result to the merchant website.
Image source: Wirecard
3D Secure allows the merchants to protect their business and for customers to protect themselves against potential payment card fraud. It establishes additional steps which guarantee to a higher extent that the transaction was authorized and therefore add certainty in the online payments. Not only does 3D Secure reduces fraud but it also makes shopping and commerce safer, sustains brand loyalty, improves overall customer confidence and increases spending online. Although 3D Secure has some limitations: not all cards are currently participating in the program authentication payer scheme and secondly, it does not restrict chargebacks to happen but reduces the cost of fraudulent chargebacks. In the case of chargeback liability, 3D Secure should not be perceived as an additional safety tool provided by the card issuer. In case of a fraudulent transaction which gets authenticated through 3D Secure the liability is transferred to the acquirer.
What is SCA and when it will becomes mandatory?
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) is a part of PSD2 in European Union and was supposed to become mandatory on 14 September 2019, while requiring all online transactions to pass an additional layer of security. On 16thof October 2019 European Banking Authority has published its opinion and pushed back the deadline for migration to SCA to 31stof December 2020. So why all the concern and fuzz around this new requirement? The SCA will bring changes to how online payments of European customers are authenticated. It establishes that each transaction must be authenticated additionally by either:
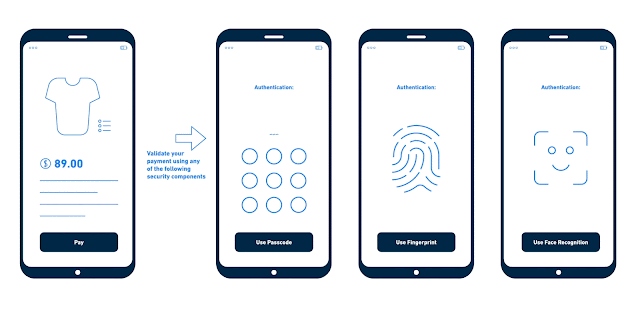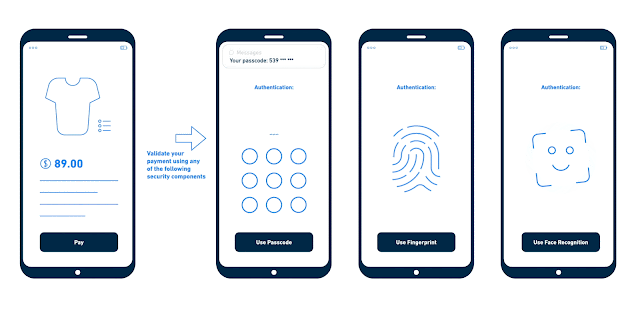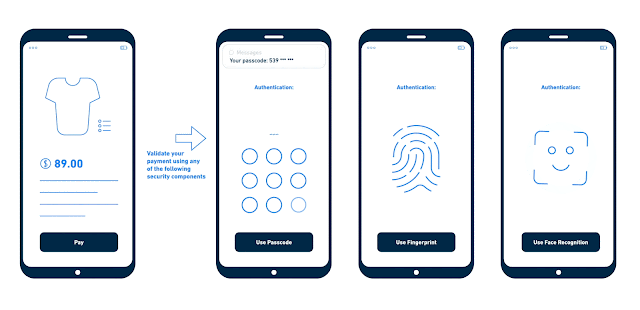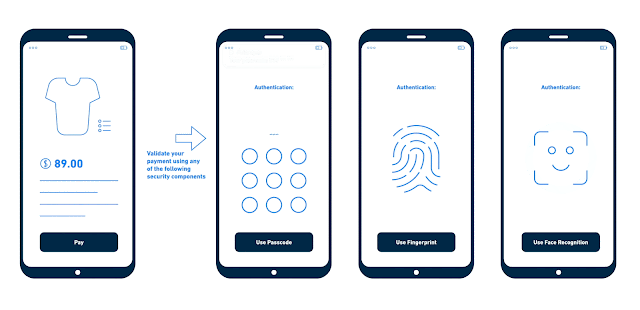
- Something your customer knows (knowledge): e.g. a PIN, password;
- Something your customer has (possession): e.g. card, smartphone; or
- Something your customer is (inherence): e.g. fingerprint, facial recognition features.
Your customers’ card issuer may decline transactions that don’t follow the new guidelines. To prepare for SCA coming into force it is crucial to determine if your business is affected and make changes before the deadline, to avoid declined payments.
The affected businesses and payments are the following:
- Business which is based in the EEAor that which createspayments on behalf of connected accounts based in the EEA
- Business serving customers located in the EEA
- Business accepting credit or debit cards issued in the EEA
Even though some of the low-risk transactions will not require SCA, the acquirer might choose to request that the customer complete the authentication. Even if you’re processing predominantly low-risk transactions, it is recommendedtointegrate with the updated version of 3D Secure so your customers can complete authentication if requested by the issuer. In the April 2019, Visa and Mastercard have deployed 3D Secure 2.0 (3DS2), an updated version dealing with the weaknesses present in the first.
The 3D Secure 2.0 main goal is to address many of the weaknesses of the previous version by offering less disruptive authentication and a better overall experience. The updated version offers new “Frictionless authentication”. It is expected to be the main card authentication method to meet the upcoming Strong Customer Authentication rules in Europe and a key mechanism for businesses to request exemptions to SCA. 3DS2 allows businesses and their payment provider to send more information on each transaction to the cardholder’s issuer. This includes contextual data, such as the customer’s device ID or previous transaction history, as well as payment-specific data like the shipping address.
This information can be used to assess the risk level of the transaction and select an appropriate response:
· The transaction will be sent through “frictionless” flow if the issuer decides that the data provided is enough to trust that the real cardholder is making the purchase and the authentication is completed without any additional authentication.
· The transaction will be sent through the “challenge” flow if the financial institution decides it needs further proof. The customer is then asked to go through additional authentication.
Image source: Magento forums
3D Secure 2.0 was initially designed after the advancement in mobile technologies making it much easier for financial institutions to offer authentication methods through mobile banking apps. The 3DS2 allows making authentication within the app while looking and feeling like a part of it. The 3DS2 offers the ability to authenticate a transaction with the help of biometric data, which is quite often currently stored on a phone. It can be either the fingerprint scanner or a facial recognition software.
3D Secure 2.0 itself can be used to request exemptions from SCA in order to avoid low-risk payment authentications. Payments which require SCA will need to go through the so called “challenge flow”, while exempted payment can be sent through the “frictionless flow” and if the payment passes through the frictionless flow, the merchant does not benefit from the liability shift for chargebacks to the cardholder/issuer.
The widespread adoption of 3D Secure 2.0 focuses mainly on individual card issuers supporting the new standard. A broader application of 3DS2 will take time and will vary by country and region. Nevertheless, the first issuers have already started supporting the updated version.
What merchants should do to be compliant and do they have any direct obligations?
Before the SCA rules enter into force, it is recommended for merchants to start preparing integration as early as possible, as there will be an increase in requests to the issuing institutions and payment providers as the deadline approaches. Despite of the recent postponement, some of the institutions have already implemented this requirement. It is advisable for all merchants to contact their payment service providers and find out how they are preparing for the changes. The payment service providers should advise and guide you if you need to update any software or make any other changes.
Merchants should distinguish the current customers’ payment flow as well and reduce friction in order not to damage the number of transactions, which are successfully passing through. Typically, e-commerce business charges customers while they are online without saving any of payment details. Adding authentication security should not be a problem if your business has the same payment flow. Customers can authenticate with 3D Secure right after they enter their payment details and placed their order.
Another crucial aspect, which merchants should consider, is the availability of exemptions to the requirement of SCA. There is a possibility to request any eligible exemptions in order for your customers not to go through the additional authentication process. However different issuers will view the exemptions differently. Therefore, it’s obligatory to design payment flows in order to authenticate customers whenever a request is sent.Exemptions include low-value transactions that total less than 30 Euros. It is limited to 150 euros, which means that after 5 successfully completed transactions, the customer would still need to go through SCA. Recurring transactions where merchants offering subscription must apply SCA only on the first transactions.
How the e-commerce payments processing industry is managing the introduction of SCA?
For payment service providers (PSP) is crucial to keep clear and effective communication with the merchants. They should advise existing and potential merchants of changes and what is currently being done to prepare for the SCA. In order to have a consistent approach, each acquirer should create a strategy for being compliant with the SCA rules.
Those payment providers, who did not yet implement 3D Secure or risk management tools, will need to invest in setting these up as soon as possible. This will determine the extent to which payment provider will need to force the application of SCA. Merchants are more likely to move to those payment providers which can keep Strong Customer Authentication application to a minimum.
Furthermore, PSP’s are also required to have constructive transaction risk assessment and monitoring, to identify fraudulent payments. Risk assessment and monitoring must allow gathering of the following data:lists of compromised or stolen authentication elements; known fraud scenarios; the amount of each payment transaction; signs of malware infection in any sessions of the authentication procedure; in the case that the access device or the software is provided by the PSP, a usage log to identify any abnormal use.
SCA exemptions are only available to PSP’s; therefore merchants should work with their acquirers to develop exemption strategies that respond to their business needs. The exemptions themselves are based on the level of the payment amount, risk score and payment channel used (please see above for available exemptions). These exemptions allow PSPs to achieve the right balance between efficiency, great customer experience, and fraud reduction. Although the issuer still retains the ability to make the ultimate decision on the applicability of the exemption to a particular transaction.
Visa has created a tool for pre-authorization status check for SCA exemption qualification, transaction risk analysis, exemption recommendation, and a reason code. This tool helps merchants and acquirers to identify low risk transactions and, in the case of remote transactions, apply for SCA exemptions. The entity that applies the exemption takes the liability for any fraudulent transaction. Therefore, it must always be approached with due caution.
Notably, 3D Secure 1.0 is still supported but it is expected that in Europe 3D Secure 2.0 will be the most used version. Card networks acknowledge that payment providers may wish to upgrade over time, and they recommend that in the meantime, 3D Secure 1.0 is used with a layered risk-based authentication approach as they move towards 3D Secure 2.0 Under such an approach. Issuers should look to implement a risk-based approach (RBA) as early as possible before upgrading to 3D Secure 2.0. Issuers should consult their Access Control Server (ACS) vendor to support and plan for this. Visa is able to offer an RBA solution that supports both 3D Secure first and second version. It should be noted that from April 2019, a merchant that has upgraded to 3D Secure 2.0 would obtain liability protection for an attempted transaction under the Visa rules if the issuer does not support 3D Secure 2.0.
What will be the impact of SCA on average consumer?
PSD2 covers not only the EEA countries but also the UK despite the Brexit as it was passed before the withdrawal. It is expected that new SCA regulations will affect over 300 million online shoppers. 3D Secure 2.0 is anticipated to speed up the process of authentication as it allows merchants to provide much more information to the issuers. This information comprises shipping/billing/IP addresses, email, browser data, merchant risk factor indicators, and etc. Comprehensive data shared between merchants and issuers improves the fraud evaluation and rate of false declines are predicted to be lower. Authenticating on the previous version of 3D Secure meant typing in a password in a pop-up window, which did not work well on mobile devices. Updated version fully depends on biometric authenticators like a fingerprint, facial recognition or one-time passwords, which in turn will speed up transactions. Now merchants will be able to turn on “challenge mode “in those cases where they want to use their own risk management models. This will denote a better and faster overall experience for customers, although merchants will have to take on the liability risk in case of a fraudulent transaction, as already stated above.
Moreover, the updated version of 3D Secure will be influenced by innovative mobile methods of authentication. Customers are expected to get used to two-factor authentication. However, at first, it could lead to some decline in successful payment rate. Mainly due to the fact that at first customers will have to register the smartphones with the payment provider so they can complete the second security step. By introducing additional steps into the checkout process there is a risk of customers just changing their mind. Even though online sellers are leaning towards neglecting customer authentication in order to secure high payment acceptance rates, they will not be able to avoid it completely. In the event that payment is not allowed for an exemption, or if the issuer doesn’t authorize an exemption, then the customer will have to go through the complete process of authentication through 3D Secure. Despite the fact that 3D Secure 2.0 underwent enhancement compared to the previous version, there are some indications that it may still cause hardship for customers.
What will be the impact of SCA on payment providers?
A study by Ravelin, analyzing millions of global transactions, revealed that 22% of payments are lost through 3D Secure, while the authentication process itself took 37 seconds on average, 91% of payments cause friction taking over 5 seconds to authenticate. Payment providers are required to implement SCA before 31 of December 2020, those who don’t fulfil requirements will start seeing their decline rates going up and conversion rate falling as issuers reject non-authenticated payments. Noncompliance with such requirements puts PSP’s at risk of losing transaction volume or even more serious consequences such as the imposition of fines or even revocation of payment provider’s license. However, there are no fines specified, as different members of the EEA are at different stages of implementation, the fine amounts may also vary.



Comments
Post a Comment